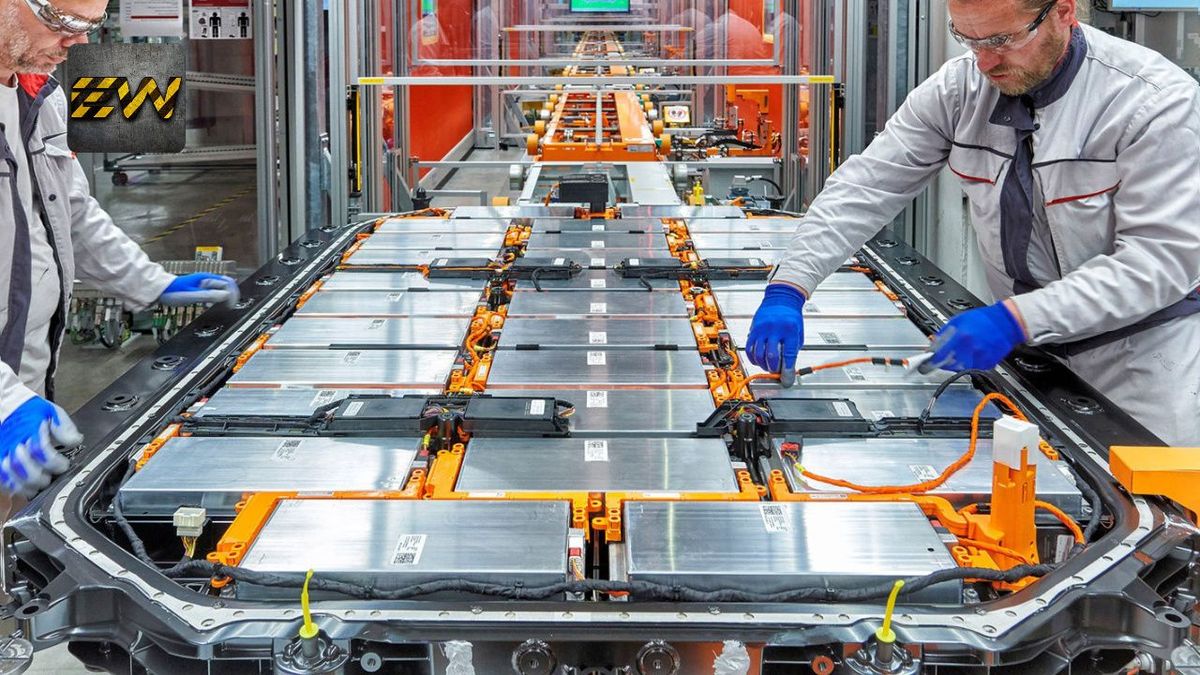

1. Introduction: Why Electric Vehicles Battery is the Core of EV Technology
Whenever we think about an electric vehicle (EV), the first thing that comes to mind is how it runs without petrol or diesel. Unlike traditional vehicles that depend on internal combustion engines and fossil fuels, EVs rely on one major component — the electric vehicles battery.
The battery is the heart of the EV. Just like our body cannot function without a heart pumping blood, an EV cannot move without its battery supplying the power. While the design, brand, and features of the car or scooter are important, what truly defines an EV’s usefulness is the battery’s capacity, life, and performance.
Key Questions Students Often Ask:
- How far can this EV travel on a single charge?
- How long will the battery last before it needs replacement?
- Is the battery safe, reliable, and affordable?
These questions are directly linked to the electric vehicles battery and its performance.
📊 According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), more than 14 million EVs were sold worldwide in 2023, and this number will grow sharply in the coming years.
As a BBA 2nd-year student writing this, I see the EV industry as more than just an automotive trend — it’s an industry that connects technology, environment, and economics. Understanding the electric vehicles battery is like understanding the backbone of the EV revolution.
In this blog, I’ll explain the basics of EV batteries, their capacity, their life span, their performance, and the future trends — all in a way that is easy to understand, with examples, student-friendly comparisons, and real-world insights.
2. Understanding Electric Vehicles Battery Basics
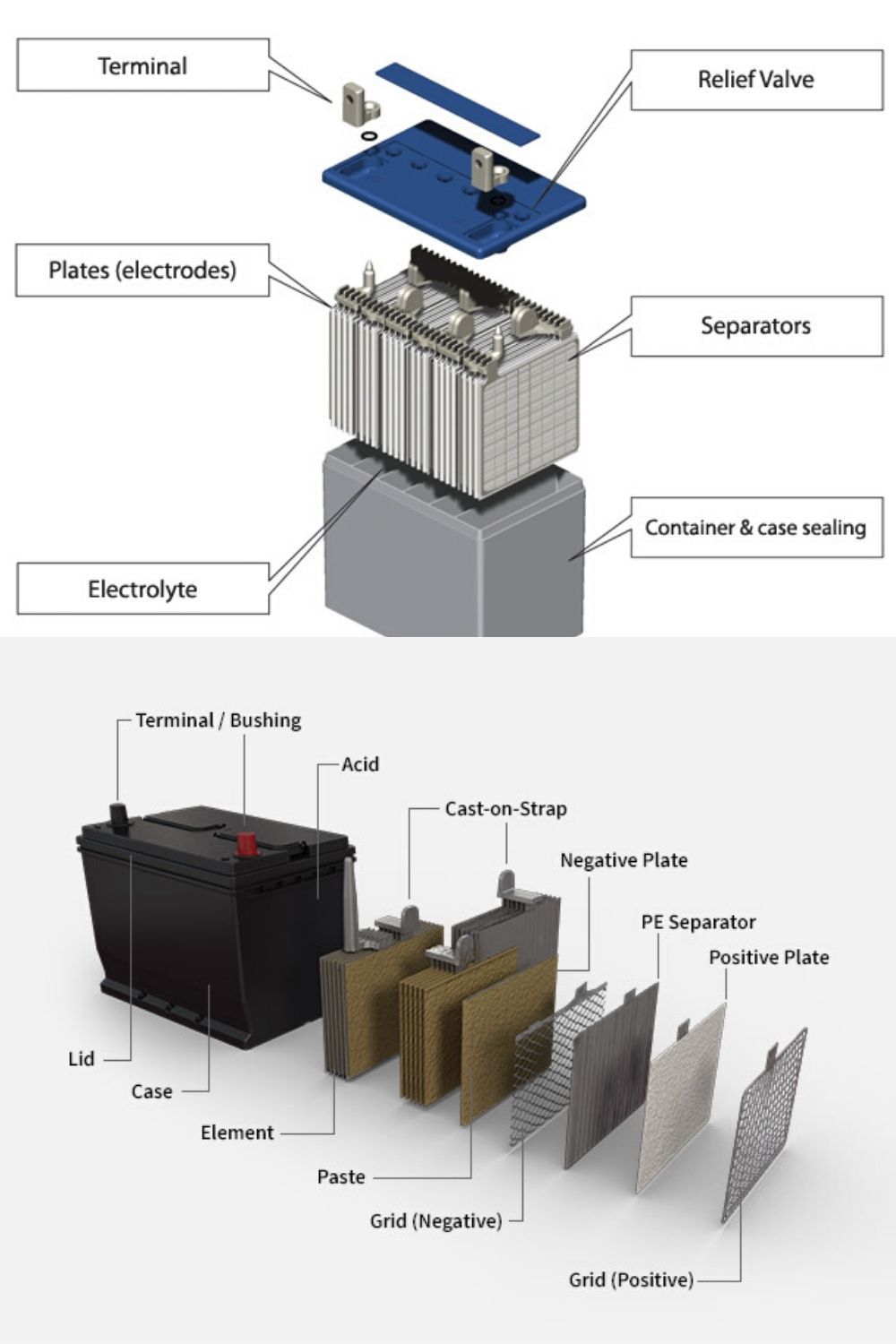
Before we dive into capacity and life, let’s understand what exactly an electric vehicles battery is.
An EV battery is a rechargeable power pack that stores electricity and supplies it to the motor that drives the vehicle. Think of it as a giant version of the battery in your smartphone — but instead of powering a screen, it powers a car, scooter, or bus.
🔋 How It Works
- Electricity is stored in the battery pack.
- When you press the accelerator, the battery supplies power to the electric motor.
- The motor converts this electrical energy into mechanical energy, which moves the wheels.
- When the battery runs low, you recharge it from a charging station or even a home socket.
⚡ Types of Electric Vehicles Battery
- Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Most common type used in EVs today.
- Lightweight, high energy density, and rechargeable.
- Found in cars like Tata Nexon EV, Tesla Model 3, and scooters like Ola S1.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
- Commonly used in hybrid vehicles.
- Longer lifespan but less efficient compared to lithium-ion.
- Solid-State Batteries (Future Tech)
- Expected to be safer, faster-charging, and longer-lasting.
- Still under research but considered the next breakthrough.
- Lead-Acid Batteries
- Used in older EVs, but they are heavy and outdated.
- Now mostly phased out except for low-cost vehicles.
👉 Student Analogy: Your EV’s performance depends on the type of battery inside it — just like your phone’s performance depends on whether it has a modern battery or an old, weak one.
3. Battery Capacity and Range: How Much is Enough?
The most common question about EVs is: How far can it go on one charge?
This depends directly on the battery capacity.
✅ What is Battery Capacity?
- Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- The higher the kWh, the more energy the battery can store.
- More stored energy = longer travel distance.
Think of it like a petrol car’s fuel tank. A bigger tank = more kilometers before refueling. Similarly, a bigger electric vehicles battery = more kilometers before recharging.
📊 Examples of Battery Capacity and Range
- Tata Nexon EV → 30.2 kWh battery → ~312 km range.
- Tesla Model S Long Range → 100 kWh battery → ~652 km range.
- Ola S1 Pro Scooter → 4 kWh battery → ~170 km range.
🎓 Student Perspective
For students like me, capacity is crucial. If I just need a scooter to travel 20 km daily to college, a small battery of 3–4 kWh is enough. But for long trips with friends, a 40+ kWh battery is better.

⛽ Comparison with Fuel Vehicles
- Petrol car with a 40-litre tank → ~600 km.
- EV with a 40 kWh battery → ~300–400 km.
- However, EV cost per km is much cheaper.
👉 Tip for Buyers: Always ask: What is the battery capacity, and how does it translate into real-world range?
4. Battery Life and Performance: How Long Do They Last?
Battery life is another big concern. Nobody wants a car that loses power in a few years.
🔋 What is Battery Life?
- Refers to how long the battery keeps working efficiently before replacement.
- Measured in charge cycles (one cycle = 0% → 100% charge).
- Most EV batteries last 1,500–2,000 cycles.
⏳ Average Battery Life Span
- Modern EV batteries → 8–10 years or 150,000–200,000 km.
- In India, Tata & Hyundai offer 8-year warranties.
- Tesla claims its batteries last 300,000–500,000 miles.
⚠️ Factors Affecting Battery Life
- Charging habits (fast charging reduces lifespan slightly).
- Temperature extremes (hot or cold).
- Driving style (aggressive driving drains faster).
- Maintenance (keeping charge between 20–80% is best).
🎓 Student Perspective
As a student, replacement costs sound scary. Tesla battery replacement may cost $10,000+ (₹8 lakh). Even in India, replacements cost ₹2–5 lakh. But with proper care, most students may never need a replacement during ownership.
👉 The good news: Battery life is improving, and future EVs may outlast petrol cars in durability.
5. Challenges and Solutions in Electric Vehicles Battery Technology
While EVs are improving fast, challenges remain.
🚗 Major Challenges
a) High Costs
- Batteries = 30–40% of EV cost.
- EVs still more expensive upfront.
✅ Solution: Prices dropped 89% (2010–2022) and continue to fall.
b) Charging Time
- Even fast charging takes longer than petrol refueling.
✅ Solution: Fast-charging infrastructure + solid-state batteries.
c) Recycling & Disposal
- Used batteries → environmental risks.
✅ Solution: Recycling firms like Attero Recycling (India) & Redwood Materials (USA) recover lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
d) Raw Material Shortages
- Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are limited.
✅ Solution: Research into sodium-ion batteries and alternatives.
6. The Future of Electric Vehicles Battery: Trends, Innovations, and Opportunities
The electric vehicles battery industry is evolving rapidly.
🌍 Upcoming Trends
- Solid-State Batteries → safer, faster, more powerful.
- AI-Based Battery Management → optimizes charging & lifespan.
- Renewable Integration → solar-powered charging reduces footprint.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) → EVs may supply power back to homes.
🎓 Opportunities for Students
- Careers in battery startups, recycling, charging stations.
- Scope in entrepreneurship & green business.
👉 Motivational Note: The next decade will belong to EV battery experts, innovators, and entrepreneurs.
7. Global Case Studies: Learning from Other Countries
🇳🇴 Norway
- 80% of new cars sold in 2023 were electric.
- Strong focus on battery efficiency + incentives.
🇨🇳 China
- Biggest EV market globally.
- CATL & BYD lead in battery innovation.
- Launching sodium-ion batteries.
🇺🇸 USA
- Tesla’s Gigafactories focus on affordable mass production.
- Leading solid-state research.
🇮🇳 India
- Catching up fast with Tata & Ola.
- Government’s FAME scheme supports EV battery development.
8. Myths and Misconceptions About Electric Vehicles Battery❌ Myth 1: EV Batteries Don’t Last Long
✅ Reality: They last 8–10 years easily, sometimes 15+.
❌ Myth 2: EV Batteries Are Unsafe
✅ Reality: Modern batteries have thermal management systems.
❌ Myth 3: Battery Replacement is Always Expensive
✅ Reality: Costs are falling, expected to be like petrol engine replacement soon.
❌ Myth 4: Charging Damages the Battery Quickly
✅ Reality: Fast charging is safe if used occasionally.
9. The Role of Recycling in Extending Battery Life
- EV batteries contain lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese.
- Recycling can recover 90% of materials.
- Second-life use: old EV batteries → solar storage.
🌱 Examples
- Attero Recycling (India).
- Redwood Materials (USA).
👉 Student View: Recycling = both sustainability + billion-dollar business opportunity.
10. Student and Youth Perspective
- Daily Use: EV scooters already cheaper than petrol bikes.
- Career Opportunities: Startups in battery tech & recycling.
- Climate Goals: Supporting EV adoption helps fight climate change.
👉 For students, understanding electric vehicles battery is not just technical — it’s a life skill for the future.
11. Looking Ahead: The Next 10 Years
- Solid-state batteries may dominate by 2030.
- EVs may cross 1,000 km per charge.
- Charging time may drop to 10–15 minutes.
- Battery costs expected to fall 50–60% more.
👉 This means EVs will not just compete but overtake petrol cars.
Conclusion
The electric vehicles battery is the driving force of the EV revolution. From capacity (how far we travel), to life span (how long it lasts), to performance (how reliable it is) — everything comes down to the battery.
For students and young professionals, this is not just about transport. It’s about careers, entrepreneurship, and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Electric Vehicles Battery
❓1. How long does an electric vehicles battery last?
✅ Most modern EV batteries last 8–10 years or 150,000–200,000 km. Some, like Tesla batteries, can last up to 500,000 miles with proper care.
❓2. How much does it cost to replace an electric vehicles battery?
✅ In India, replacement costs range from ₹2–5 lakh, depending on the car model. Globally, premium EV battery replacements like Tesla may cost around $10,000 (₹8+ lakh). The good news is costs are falling every year.
❓3. What is the difference between battery capacity and battery life?
✅ Battery Capacity = How much energy the battery can store (measured in kWh), which decides the range.
✅ Battery Life = How long the battery remains efficient before replacement (measured in years or charge cycles).
❓4. Is fast charging harmful for electric vehicles battery?

✅ Occasional fast charging is safe. Modern EVs have battery management systems that prevent overcharging. However, regular slow charging at home is healthier for long-term battery life.
❓5. Can an ?
✅ Yes. EV batteries are full of valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Recycling companies like Attero Recycling (India) and Redwood Materials (USA) are recovering up to 90% of materials. Old batteries can also be reused in solar energy storage.
❓6. What affects the performance of an electric vehicles battery?
✅ Major factors include:
- Driving style (aggressive driving drains battery faster).
- Charging habits (keeping between 20–80% is ideal).
- Weather (extreme heat or cold reduces efficiency).
- Age of the battery.
❓7. Will future EV batteries be better than today’s?
✅ Yes! By 2030, we may see:
- Solid-state batteries with higher range.
- Charging times reduced to 10–15 minutes.
- EV ranges crossing 1,000 km on a single charge.
- Much cheaper battery costs.
